close
Choose Your Site
Global
Social Media
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-07-25 Origin: Site
Power cables are essential for powering everything from homes to industries. But how can you tell if a power cable is AC or DC? In this article, we'll explore the key differences between AC and DC cables. We'll also guide you on how to identify and test power cables for their type.
AC (Alternating Current) and DC (Direct Current) power cables are designed to transmit electrical power, but they differ in the type of current they carry. AC cables are used for alternating current, where the direction of the current periodically changes. These cables are commonly used in power grids to distribute electricity across long distances.
DC cables, on the other hand, are designed to handle direct current, where the flow of electricity remains constant and unidirectional. DC cables are often used in battery-powered devices, solar panels, and other low-voltage systems.
Differences between AC and DC cables include the type of current they transmit, as well as their structural design and insulation requirements.
AC and DC cables function differently due to the nature of the current they carry. AC cables handle alternating current, which constantly changes direction. This alternating flow allows AC to be transmitted efficiently over long distances, especially with the use of transformers.
DC cables, on the other hand, carry direct current, which flows steadily in one direction. DC is typically used in systems where a constant and stable power supply is necessary, such as in solar energy systems, electric vehicles, and certain electronic devices.
How AC and DC cables work: AC cables facilitate the transmission of fluctuating electrical current, while DC cables provide steady power for specific applications.
One of the easiest ways to distinguish between AC and DC cables is by looking at the markings or labels on the cable. Many cables include symbols that specify whether the cable is intended for AC or DC power. AC cables typically feature the "~" symbol, representing alternating current, and are often found in power lines and electrical outlets. Conversely, DC cables will typically have a "-" or "DC" marking, indicating the use of direct current.
These markings are often found along the outer sheath of the cable, making them easy to spot. This quick visual check can save you time and help avoid confusion.
Another method to identify whether a cable is AC or DC is by examining the number of wires inside the cable. AC cables, especially in three-phase systems, will typically contain three or more wires. These wires are used to carry alternating current across different phases, ensuring that the power supply is balanced and efficient. For single-phase AC systems, the cables generally have two wires: one live (hot) wire and one neutral wire.
On the other hand, DC cables usually have two wires, a positive (+) and a negative (-) wire, that carry the current in a single, steady direction. DC cables are commonly used in systems like solar panels, batteries, and electronic devices where consistent power is needed.
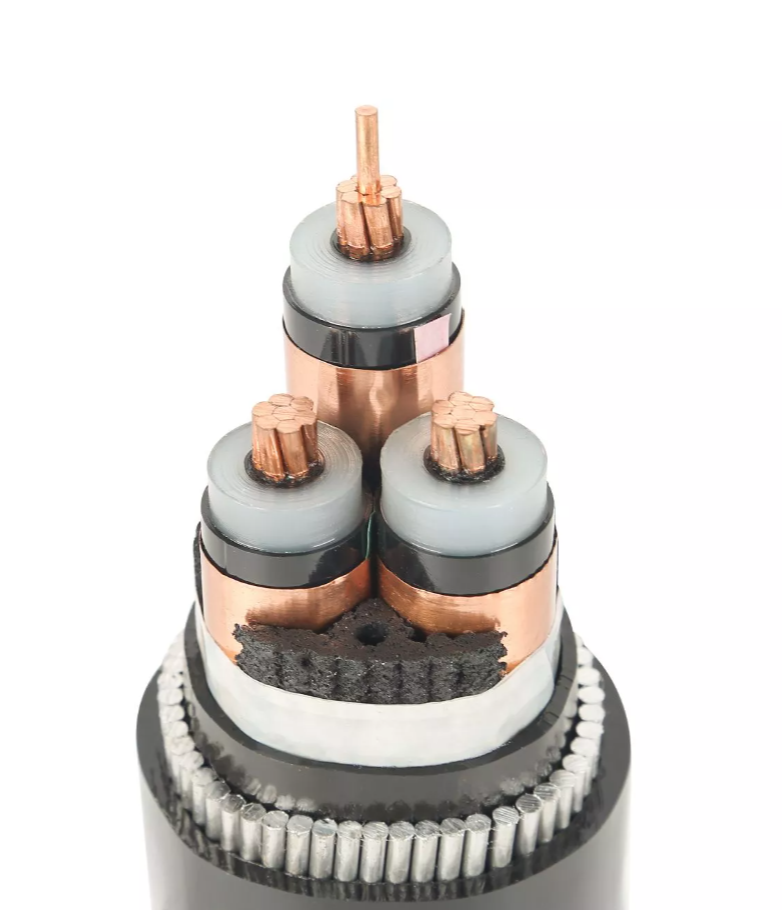
The type of insulation used in the cable is another factor that can help identify whether it is an AC or DC cable. AC cables tend to have thicker and more robust insulation to protect against the alternating voltages and prevent electrical faults. The insulation is designed to handle voltage fluctuations that occur in AC systems.
In contrast, DC cables often use simpler insulation, as DC power has a constant voltage and flows in one direction. DC cables typically require less insulation material since they don't have the same voltage variations as AC cables. Insulation materials like PVC, rubber, or XLPE (cross-linked polyethylene) are commonly used in DC cables due to their ability to handle constant voltage.
The type and thickness of insulation used in the cable can tell you if it is meant for an alternating current or a direct current application.
While markings, wire count, and insulation are some of the most straightforward methods for identifying AC and DC cables, there are other ways to test or visually check the cables. For instance, specialized voltage testers and multimeters can help confirm whether the cable is carrying AC or DC. Additionally, in industrial setups, some cables are labeled with clear specifications, indicating their voltage and current type.
Remember, safety should always be a priority when dealing with electrical cables. Always check for proper cable markings and when in doubt, use the appropriate testing equipment to confirm the cable type before installation or use.
A multimeter is a useful tool for determining whether a power cable carries AC or DC. Here's a simple step-by-step guide:
1. Set the Multimeter: Set the multimeter to measure voltage (V) and choose either AC or DC mode.
2. Connect the Multimeter: Place the multimeter probes on the cable's positive and negative terminals.
3. Read the Display: Observe the reading on the multimeter's display. If the voltage fluctuates, it's AC. If it remains stable, it's DC.
Testing AC or DC cables with a multimeter: By measuring voltage fluctuations, you can quickly identify whether the cable is carrying alternating or direct current.
Another way to identify AC or DC cables is by looking at the voltage characteristics. AC voltage fluctuates continuously, forming a sine wave pattern, which can be observed on an oscilloscope or through a multimeter with a frequency reading. This wave moves from positive to negative in cycles, indicating alternating current.
In contrast, DC voltage is steady, remaining at a constant level in one direction, making it ideal for devices that require uninterrupted power.
AC vs DC voltage characteristics: AC voltage fluctuates over time, while DC remains constant and unidirectional, making it easy to distinguish using a multimeter.
One common mistake when identifying AC and DC cables is confusing their insulation or markings. For example, both types of cables can look similar, especially if they are part of a bundled system. However, the insulation and outer sheath of the cable are often labeled differently, which can be misleading.
Another common mistake is assuming that all cables with two wires are for DC. While DC cables often have two wires, some AC cables, particularly in smaller applications, may also have two wires.
AC and DC cables should not be used interchangeably. Each cable is designed for a specific current type, and using the wrong one can result in electrical hazards. For example, AC cables are built to handle alternating current, which frequently changes direction. In contrast, DC cables are made to carry a steady, unidirectional flow.
Using the wrong cable for the wrong current type can lead to overheating, electrical fires, or equipment failure. It's important to match the cable with the system's current type to ensure safety and functionality.
AC and DC cables are designed for specific current types and should not be mixed to avoid risks.
Using the wrong type of cable can have serious consequences. If you use an AC cable for a DC application, or vice versa, it can lead to overheating, short circuits, and even fires. Each type of cable is designed to handle the specific current flow of either AC or DC. Using the wrong cable not only reduces efficiency but also poses safety risks, as improper insulation and conductor materials can fail under the wrong electrical conditions.
AC cables are widely used in power transmission grids, where they help deliver electricity over long distances efficiently. AC's ability to easily change voltage using transformers makes it perfect for large-scale energy distribution. This helps minimize energy losses and allows for the efficient delivery of electricity to homes and businesses.
DC cables are essential in solar energy systems, electric vehicles, and low-power electronics, where a steady, uninterrupted current is required. DC is more efficient in these systems because it provides a constant flow of power, which is ideal for charging batteries or powering sensitive electronics.
To distinguish between AC and DC power cables, check their structure, insulation, and voltage characteristics. AC cables often have multi-wire designs, while DC cables have simpler two-wire setups.
Choosing the correct cable is essential for safe and efficient power distribution. How to identify AC or DC cables depends on understanding these differences and matching them to the correct application.
East Energy Electrical Engineering has years of experience in designing and manufacturing customized cables. If you want to know more about cables, feel free to contact us anytime with your inguiries.

A: DC power transmission is more efficient for short distances and systems requiring stable, continuous power, such as solar and battery-operated devices.
A: Check the labeling on the cable, or use a multimeter to test for fluctuating (AC) or stable (DC) voltage. AC cables often have more complex insulation and multiple wires.
A: AC is easier to transform to different voltage levels, reducing energy loss over long distances, making it more suitable for widespread distribution.