close
Choose Your Site
Global
Social Media
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2026-01-09 Origin: Site
You use low voltage power cables every day. You turn on a lamp at home. You use machines at work. These cables handle voltages from 0 to 600V. They help low voltage systems work safely. Picking the wrong cable can be dangerous. It might cause a fire. It could waste energy. It may harm your devices. You must choose the right cable for your space. This is important for low-voltage signals. It matters for heavy equipment too. Cables from East Energy Electrical Engineering Co., Ltd. (4E) are reliable. They give you quality in every installation.
Low voltage power cables work safely up to 600V. This makes them good for homes and factories.
Picking the right cable is very important. The wrong cable can cause fires or break machines.
Cables use different materials like copper and aluminum. These change how well the cable works and how much it costs. Always check what the cable is made of before you buy it.
Cables for homes are simple and cost less. Cables for factories last longer and handle more power. They also work in tough places.
Always check for safety marks like UL or NEC. These show the cable is safe and follows rules.
Low voltage cables are everywhere, like in homes and factories. These cables carry electricity at lower voltages. This makes them safer for people to use and install. Most people say low voltage is below 600 volts. But some rules use different numbers.
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) says low voltage is 0 to 1000 volts AC or 0 to 1500 volts DC.
IEC 60038 says supply system low voltage is 50 to 1000 volts AC or 120 to 1500 volts DC.
In the United States, the National Electrical Code (NEC) says low distribution system voltage is 0 to 49 volts.
Most low voltage power cables are rated up to 600 volts. This covers most lights, outlets, and small machines at home or work. These cables are safer to handle than high voltage ones. You do not need special training for many low voltage cables. This is why people use them for DIY projects.
Tip: Low voltage wiring costs less and is easier to put in than high voltage wiring. You save money on parts and work. You also lower the chance of getting shocked, which keeps you and your family safe.
Low voltage cables use different materials for safety, price, and how well they work. You should know what is inside your cable before you pick one. The table below shows the most common materials and what they do for your cable:
Material Type | Impact on Performance and Safety |
|---|---|
Copper | High conductivity reduces energy loss; flexibility eases installation. |
Aluminum | Lower weight cuts costs; requires larger size for same conductivity. |
PVC | Flexible, flame-resistant, and affordable; used for insulation and outer sheath. |
XLPE | Handles heat and stress well; used for insulation. |
Aluminum Foil | Blocks EMI effectively but is less flexible; used for shielding. |
Braided Copper Wires | Offers flexibility and good EMI protection; used for shielding. |
PE and PO | Resist moisture and chemicals; used for outer sheath. |
Most low voltage cable wire uses copper. Copper carries electricity well and bends easily. Aluminum is cheaper and lighter, but you need a thicker cable for the same job. For insulation, you see PVC and XLPE. These keep electricity inside and protect you from shocks. Some cables have extra layers, like aluminum foil or braided copper, to block interference from other devices.
You should always check the materials before you buy a low voltage electrical cable. Picking the right one helps your system last longer and work better. For outside or wet places, look for cables with PE or PO sheaths. These stop water and chemicals from getting in.
People use low voltage cables in many places because they are safe, bendy, and save money. You do not need special tools or skills to put in most 600v low voltage cable types. This makes them great for lights, outlets, and small machines. When you pick the right low-voltage cables, you protect your devices and save money.
Low voltage cables for homes and factories are not the same. Cables for homes have a simple build. They use one layer of insulation and a basic cover. These cables go inside walls or ceilings. They do not face much damage. You can bend them easily. They fit into small spaces.
Cables for factories are much stronger. They are used with big machines, oil, and heat. These cables have extra layers, like steel armor or thick covers. The extra layers protect the cable from cuts and fire. Some cables use special materials to stop water or chemicals. You see armored low voltage cable wire in factories. This type lasts longer and works well in tough places.
Note: Using a home cable in a factory is not safe. Always pick the right cable for the place.
You need to know how much power your cable will carry. In homes, low-voltage cables power lights and small devices. These do not need much electricity. Home cables are smaller and have a lower amp rating. A 600v low voltage cable is enough for most homes.
Factories use more power. Machines and control panels need thick low-voltage cables. These cables carry more current without getting too hot. Factory cables have bigger copper or aluminum cores. This helps them handle heavy loads safely.
Here is a table to show the difference:
Setting | Typical Load (Amps) | Cable Size (mm²) | Example Use |
|---|---|---|---|
Residential | 10-32 | 1.5-6 | Lighting, outlets, HVAC |
Industrial | 32-200+ | 6-120+ | Motors, machines, panels |
If you use a cable that is too small, it can get hot and start a fire. Always check the load before picking a low voltage electrical cable.
Safety rules keep people and buildings safe. Home low-voltage cables must follow local codes. These codes help stop fires and make sure cables are safe. You will see marks like UL or ETL on home cables. These marks mean the cable passed safety checks.
Factory low-voltage cables must follow stricter rules. Factories have more dangers, so the rules are tougher. You may see standards like IEC, NEC, or IEEE. These rules check for flame, chemical, and strength safety. Some factory cables must pass tests for oil, water, and even animals.
Tip: Always look for safety marks on your cables. Certified low-voltage cables keep your system safe and legal.
You want to save money and energy. Home low-voltage cables cost less because they use less material. They work well for short runs and small loads. You do not need to pay for extra features you will not use.
Factory low-voltage cables cost more at first. They use more copper or aluminum and have extra layers. But they last longer and help avoid problems. Good factory cables also waste less energy. Thick wires and good insulation help you save on bills.
Remember: The right cable saves you money over time. Do not use a cheap cable for a hard job. Buy quality for safety and to save energy.

There are two main types of low voltage cables. The types depend on how many conductors they have. Single-core cables have just one conductor inside. Multi-core cables have two or more conductors in one cable. A 2 core low voltage cable is good for simple lights or power. A 3 core low voltage cable works for three-phase systems or control wiring. Sometimes, a 4 core low voltage cable is used in factories.
Here is a table to compare single-core and multi-core low voltage cables:
Feature | Single-Core Cables | Multi-Core Cables |
|---|---|---|
Thermal Management | Cool down 25% faster | Less effective in heat dissipation |
Current Carrying Capacity | Higher, good for heavy loads | Needs current derating of 10-15% |
Space Efficiency | Uses 40-60% more conduit space | Saves about 34% conduit space |
Application | Best for industrial uses | Great for building systems and control panels |
Installation Complexity | More rigid, harder to route | Flexible and easier to install |
Single-core cables are best for big factory jobs. Multi-core cables help keep wires neat in control panels. They also make it easier to avoid wiring mistakes.
Low voltage cables can be armored or unarmored. Armored cables have a metal layer for extra protection. This layer keeps them safe from damage, water, and animals. You can use armored cables underground or in rough places. Unarmored cables do not have this metal layer. They are lighter and bend more easily.
Here is a quick comparison:
Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
Armored | Strong, safe in tough spots, resists rodents and water | Heavier, costs more, harder to install |
Unarmored | Cheaper, flexible, easy to install, saves space | Less protection, shorter lifespan |
Armored low voltage cables are good when you need extra safety. Unarmored low voltage cables are better for indoor jobs with less risk.
You use low voltage cables every day at home. They power your ceiling lights and lamps. These cables also work for outlets that charge your phone. Most home lighting uses 2 core or 3 core low voltage cable. These cables fit behind walls and ceilings easily. You can put them in with simple tools. Low-voltage cables help save energy and keep your home safe. A 600v low voltage cable is good for most lights and outlets. If you want to light your garden or driveway, use low voltage outdoor cable. This cable stands up to water and sunlight.
Tip: Always check the cable rating before adding new lights or outlets. The right low voltage power cables stop overheating and keep you safe.
Low voltage cables are important for home security and communication. You use them for doorbells, cameras, and alarms. These cables carry signals at lower voltages. This makes your system safer and more reliable. Here are some reasons to use low-voltage cables for security and communication:
Lower electrical risks help keep your family safe.
Using less power saves money on your bills.
Your system lasts longer and needs fewer repairs.
Better safety standards meet strict rules.
Good cables give strong signals for alarms and cameras.
You often see multi-core cables, like 4 core low voltage cable, in security systems. These cables let you connect many devices with one wire. You can run them through walls or outside for cameras and sensors.
You need low voltage cables for HVAC controls and big appliances. Most thermostat wires use 18 AWG stranded copper because it bends easily. HVAC systems often use 24V AC, so low-voltage cables are perfect for thermostats and control panels. You can use 2 core low voltage cable for simple thermostats. Use 3 core low voltage cable for more advanced models. For underground or outdoor jobs, pick cables with THWN or UF insulation. These types keep out water and last longer.
Common HVAC wire sizes: 14 AWG to 18 AWG.
Stranded wire bends well in tight spots.
Multi-conductor copper cables connect smart thermostats.
Always check if your thermostat uses low-voltage or line-voltage wiring.
Low voltage cables also power doorbells, yard lights, and small appliances. You get safe and strong connections that last a long time.
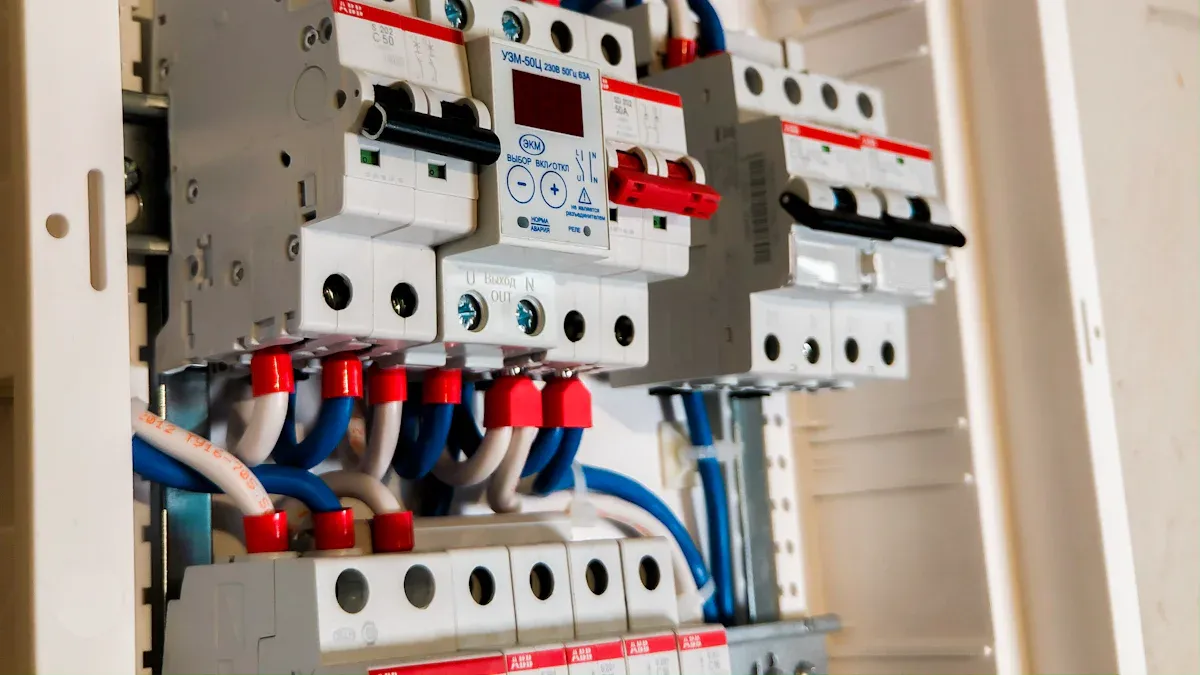
Low voltage cables are used a lot in factories. They help connect parts so machines can work together. You use these cables to join sensors, switches, and control panels. Here are some ways low-voltage cables help in control circuits:
Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) systems use these cables. They connect sensors, actuators, and human-machine interfaces. This helps you automate many jobs in the factory.
Fire alarm and life safety systems need supervised low voltage circuits. These circuits help keep your building safe during emergencies.
Building automation systems (BAS) use low voltage networks. They control heating, cooling, and ventilation. This makes your factory more comfortable and saves energy.
You often pick 2 core low voltage cable or 3 core low voltage cable for these jobs. These cables fit well in control panels and make wiring easy.
Low voltage power cables are important for small machines. You use them to run motors, pumps, and conveyor belts. These cables give safe and steady power. They have strong insulation and high-purity copper inside. This makes them flexible and tough against water and damage. You can use these cables inside or outside, even in hard factory places.
Low voltage cables rated up to 1 kV work well for main power circuits. You often use 2 core low voltage cable for simple machines. For more complex setups, you use 3 core low voltage cable. If you need to power outdoor machines, you pick low voltage outdoor cable. These cables can handle rain and sun. They also help stop fires, which keeps your workplace safe.
Factories need low-voltage cables for data and automation. These cables power smart machines and help them talk to each other. You use them for fast Ethernet with Cat6a cabling. You also use 24VDC control wiring to link sensors, actuators, and PLCs. This lets you control machines right away.
Low voltage cables help you watch power and collect data from meters and sensors. You can use 4 core low voltage cable for big data and automation systems. These cables help your factory work smarter and faster.
You need to pick the right cable for your system. First, check the voltage and current it will carry. If you use the wrong cable, it can get too hot or even catch fire. Here are some things to think about:
Electrical load: Find out how much current your system uses.
Voltage rating: Make sure the cable can handle your system’s highest voltage.
Voltage drop: Long cables can lose voltage and not work as well.
Environmental conditions: Think about if the cable will be inside, outside, or in wet places.
Compliance and rules: Always follow safety rules from your area and the world.
The right cable size and rating help stop overheating and wasting energy. Cables with good energy efficiency ratings save power and lower your bills.
Insulation and sheathing keep your cable safe and make it last longer. Good insulation slows down fire and keeps away bad smoke. Many cables use materials that block water, chemicals, and sunlight. This helps your cable stay safe in hard places. Strong sheathing also protects against heat, water, and damage.
Stops fire and smoke from spreading
Blocks chemicals, water, and sunlight
Stays strong in hot and rough weather
Always check the insulation type before you buy. This keeps your system safe and working for a long time.
Look at how many cores your cable has. More cores let you connect more things or run bigger circuits. Flexible cables are easier to put in, especially in small spaces or around corners.
More cores help with bigger projects
Flexible cables make setup faster and easier
You must use cables that meet safety and quality rules. The table below shows some important certifications:
Certification/Standard | Description |
|---|---|
National Electrical Code (NEC) | Sets rules for safe electrical installations |
Underwriters Laboratories (UL) | Tests and lists cables for safety and performance |
National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) | Covers fire safety for wiring and alarm systems |
RoHS Compliance | Limits hazardous materials for environmental safety |
Tip: Always look for these marks on your cable. Certified cables keep your home or factory safe and legal.
Low voltage power cables are important at home and in factories. They help run lights, security systems, and control equipment safely. These cables help you save money and lower risks. You can use them for many different jobs.
Always check your local rules before buying or installing cables. Look for standards like NEC or TIA/EIA.
Try new technology and learn about smart home or security systems.
If you want good cables, East Energy Electrical Engineering Co., Ltd. (4E) in Yixing, China, has many choices. 4E has strong brands, modern factories, and lots of trade experience. They give you quality and custom cables for any project.
Low voltage power cables work for systems up to 600 volts. Most homes and factories use cables in this range. These cables make your electrical systems safe and simple to set up.
You should not use home cables in factories. Industrial cables have stronger insulation and more protection. These things help them last longer and handle hard jobs.
You need cables with waterproof covers and UV resistance. Look for labels like "outdoor rated" or "UF" on the cable. These features help your cables stay safe in rain and sun.
Multi-core cables connect many devices at the same time. These cables help you keep wires neat and avoid mistakes. Multi-core cables are good for control panels and security systems.
You should look for marks like UL, NEC, or RoHS. These marks show the cable meets safety and quality rules. Certified cables help keep your home or factory safe.