close
Choose Your Site
Global
Social Media
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-12-10 Origin: Site
Choosing the right high voltage power cables is crucial for ensuring the safety, efficiency, and longevity of electrical systems. Whether for overhead or underground applications, the cables you select play a key role in grid reinforcement, renewable energy integration, and meeting the rising demand for electricity. In this article, we’ll guide you through the key factors to consider when selecting the right high voltage cables. You’ll learn how to make an informed decision that ensures optimal performance and reliability for both overhead and underground installations.
For top-quality cables, 4E offers reliable solutions designed for efficiency and durability. Learn more about our products to optimize your energy transmission systems.
To understand how to choose the right high voltage power cables, it’s important to first know what they are and how they function in electrical systems.
High voltage power cables are designed to carry electrical power at voltages above 1,000 volts, typically ranging from 35kV to 500kV and beyond. These cables are essential for transmitting electricity over long distances, connecting power plants, substations, and consumers. They ensure that large amounts of electricity can be safely and efficiently transported across the grid.
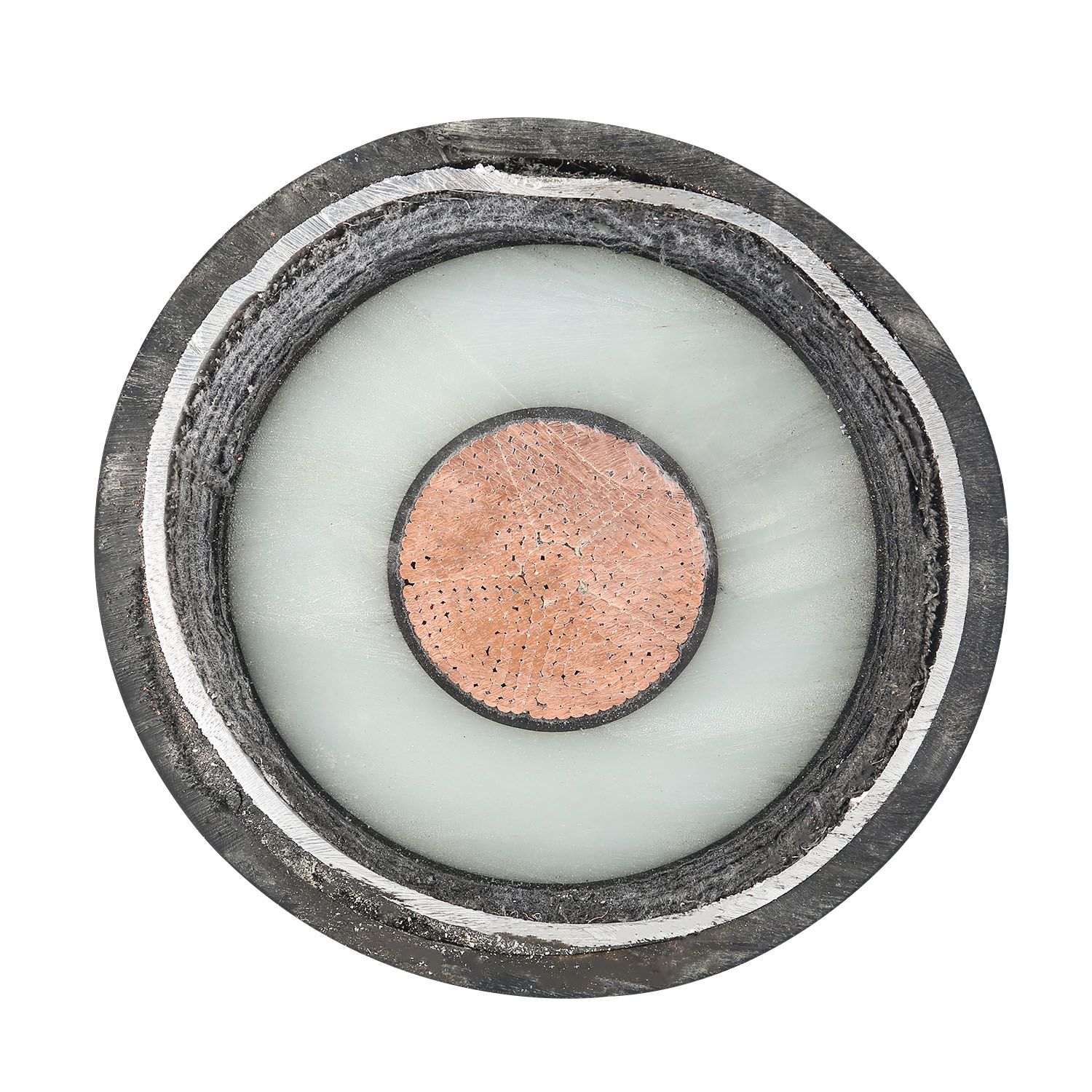
High voltage power cables consist of multiple components, including a conductor, insulation, shielding, and an outer protective sheath. The conductor is typically made of copper or aluminum and is responsible for carrying the electrical current. The insulation layer prevents electrical leakage, while the shielding protects against external interference. The outer sheath serves as a protective barrier against physical damage and environmental factors.
● Conductor: Transports electricity, typically made from copper or aluminum for maximum conductivity.
● Insulation: Prevents leakage and ensures safety by containing the electrical current.
● Shielding: Minimizes external interference and ensures the integrity of the cable’s function.
● Outer Sheath: Protects the cable from physical damage and environmental exposure such as moisture or UV radiation.
There are several important factors to keep in mind when selecting the right high voltage power cables for overhead and underground applications.
Before choosing high voltage power cables, you must first understand the required voltage rating for your system. Ensure the cables can handle the necessary current capacity without excessive heat generation or loss of power. Choosing the correct voltage rating is crucial for system safety and performance.
Application | Typical Voltage Rating | Common Insulation Material | Recommended Use |
Overhead Cables | 35kV - 500kV | XLPE, EPR | Suitable for rural, open areas; exposed to weather conditions |
Underground Cables | 35kV - 220kV | XLPE, Paper Insulated Lead Covered (PILC) | Suitable for urban areas, resistant to soil pressure and moisture |
● Overhead cables must be able to withstand environmental elements like rain, strong winds, and extreme temperature changes.
● Underground cables need to be resistant to moisture, soil pressure, and chemical exposure. These cables often require additional protection layers to ensure longevity.
The insulation material is a crucial component in high voltage cables. It determines the cable's ability to withstand electrical stress, temperature variations, and environmental exposure. Choose cables with insulation materials that meet your system’s electrical and environmental requirements to ensure safety and durability.
Ensure the insulation material and conductor selection align with your voltage and environmental conditions to optimize cable performance and reduce potential risks.
Deciding whether to use high voltage cables for overhead or underground applications depends on various factors, including the specific site conditions and requirements.
● Overhead cables are often used in areas where space is not constrained and are ideal for open, rural areas or regions with low population density.
● These cables need to be robust, able to withstand extreme weather conditions like high winds, rain, and snow.
● Underground cables are typically used in urban environments, where space is limited, or aesthetics are a concern.
● They must be capable of handling moisture, soil pressure, and chemical exposure. Additional protective layers are necessary to shield the cables from these elements.
Factor | Overhead Cables | Underground Cables |
Space Requirements | Minimal space needed | Requires trenching and more space |
Weather Resistance | Must withstand harsh weather (wind, rain) | Must withstand soil pressure, moisture, chemicals |
Installation Environment | Open, rural areas, or regions with low population density | Urban areas, aesthetic or space concerns |
Protection Requirements | Robust shielding and weatherproof materials | Additional protective layers for moisture, soil pressure |
When selecting high voltage power cables, it’s important to ensure that they meet the relevant technical specifications and industry standards.
● The voltage rating of the cable must match your system’s requirements. For high voltage applications, the cables should have insulation that can handle high electrical stress without degrading.
● Ensure the cables comply with industry standards such as IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) or IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers). These certifications ensure that the cables meet safety, reliability, and performance standards required for high voltage systems.

While cost is an important factor in selecting high voltage power cables, it should not come at the expense of safety or efficiency.
● Underground cables tend to have higher initial installation costs compared to overhead cables due to the need for trenching and extra protective layers. However, they often have lower maintenance costs over time as they are less exposed to environmental damage.
● Overhead cables, while less expensive to install, may require more frequent maintenance due to exposure to environmental factors.
● High voltage cables that are durable and made from high-quality materials will provide long-term value, reducing the need for frequent repairs and replacements. This durability is particularly important in grid reinforcement, where cable longevity is a critical consideration.
Cost Factor | Overhead Cables | Underground Cables |
Installation Cost | Lower (Less labor-intensive, no trenching) | Higher (Requires trenching, extra protective layers) |
Maintenance Cost | Higher (Frequent repairs due to environmental exposure) | Lower (Less exposure to environmental damage) |
Long-term Durability | Medium (Exposed to weather, more prone to damage) | High (Protected from environmental factors, longer lifespan) |
High voltage power cables are used in various critical applications that reinforce and optimize the electrical grid.
● High voltage power cables are a key part of power transmission networks, connecting power plants to substations and distributing electricity to consumers. These cables minimize energy losses and ensure that the power supply is reliable and efficient.
● High voltage power cables are essential for transmitting energy from renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar farms, to the grid. These cables connect energy generation facilities in remote areas to urban centers, enabling the integration of renewable energy into the grid.
● In industrial applications, high voltage cables are used to supply electricity to factories and large commercial buildings, ensuring reliable power for heavy machinery and large-scale operations.
● Underground cables are suitable for areas where visual aesthetics or space limitations make overhead cables impractical. Submarine cables are used to transmit power under bodies of water, such as across lakes or between offshore wind farms and the mainland.
For remote or hard-to-reach locations, consider submarine or underground cables for efficient and reliable power transmission.
High voltage power cables are essential for reinforcing electrical grids, improving transmission efficiency, and ensuring system reliability.
● High voltage cables enable the transmission of power across great distances, reducing energy losses and allowing electricity from distant power plants to reach urban centers and industries efficiently.
● As energy demand continues to increase, especially in industrialized and urban areas, high voltage power cables help accommodate this growing demand, ensuring that the grid can handle higher loads without compromising stability.
● High voltage cables help increase grid flexibility and resilience, ensuring that the system can handle fluctuations in power generation and consumption. This is especially important as more renewable energy sources are integrated into the grid.

Advancements in high voltage cable technology will continue to shape the future of grid reinforcement and energy transmission.
● The development of superconducting cables, improved insulation materials, and enhanced shielding techniques promises to improve transmission efficiency and reduce power loss, making high voltage power cables even more efficient.
● High voltage cables are integral to the development of smart grids, which allow for real-time monitoring and management of energy flow. As smart grids evolve, these cables will play a central role in ensuring efficient energy distribution.
Invest in high voltage power cables that are compatible with smart grid technologies to ensure your infrastructure is future-proof and adaptable to changing energy needs.
Choosing the right high voltage power cables is crucial for grid reinforcement. These cables help reduce energy loss, increase power capacity, and enhance the overall reliability of the grid. Whether for power transmission, renewable energy integration, or industrial applications, high voltage power cables are vital for modernizing energy infrastructure. 4E offers durable and reliable cable solutions designed to meet the evolving needs of power systems, ensuring long-term performance and efficiency.
A: For overhead installations, choose high voltage power cables with weather-resistant insulation, robust shielding, and UV protection to withstand environmental stress like rain, wind, and extreme temperatures.
A: When choosing underground high voltage cables, consider moisture resistance, chemical protection, and durability against physical stress, as these cables are exposed to soil pressure and moisture.
A: XLPE cables are commonly used for high voltage power transmission because of their high thermal resistance, low dielectric losses, and ability to withstand higher temperatures and electrical stress.
A: Overhead cables are typically cheaper and easier to install, while underground cables provide better protection against environmental damage and are ideal for densely populated areas or challenging landscapes.